drylin® XY linear tables
XY-tables enable the horizontal movement of automated machines such as assembly robots in production plants, milling tables or drilling tables. Robotic arms and other automated machines have limited range of motion while their bases remain fixed; XY-tables allow these bases to move horizontally in the X and Y directions. Also known as cross slides, these XY-tables are both manual and motorised positioning tables with linear motion based on bearings set in motion by a drive mechanism. Typically, the drive is implemented by a linear motor or a hand wheel. XY-tables are designed to enable powerful positioning along multiple axes.
Contact the expert
XY-table options
drylin SHT XY-tables
- Available as standard and pre-loaded version
- Adjustments by trapezoidal thread
- Upper unit can be aligned right or left
Visit the shop
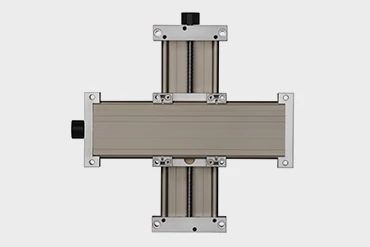
drylin SLW XY-table
- Hard anodised aluminium drylin W guide rail
- Pre-loaded version SLWE-XY-PL also available
- Accessories available
Visit the shop

drylin SLW XY-table | Stainless steel
- High torsional stability
- For manual adjustments
- Compact and low-profile
Visit the shop
Accessories for XY-tables
Hand wheels for lead screw drives
For various requirements, igus has a wide range of hand wheels available from stock; from small compact sizes up to 125 Ø with/without handles in different designs.- Rotary knob: defined standard for complete units
- Different outer diameters available
- Different handles available
- Also available as rinsable and corrosion-free stainless steel version
Hand wheels for XY-tables
Position indicator
The position indicator for linear axes is used for setting and direct reading of the carriage position. This can reduce downtime, perform adjustments quickly and accurately, and reproduce values.- Can be combined with manual clamps and hand wheels
- Reduction sleeves included in delivery
- Available in the required counting and viewing direction and in a variety of colours

Lead screw clamps
Linear modules with trapezoidal threads are equipped with a self-locking mechanism. Many applications call for an additional clamping option as an extra safeguard against unintentional movement of the lead screw.- Shaft clamp adapter for attaching to the position indicator and subsequent clamping of the lead screw.
- Material: polymer housing with aluminium shaft clamp
- Reduction sleeves for further diameters available
Lead screw clamp for XY-tables
Angular drive
igus provides a product range of continuously rotatable angular drives for adjustment options from a defined direction. For manual adjustments, the angular drives can also be configured with position indicator, clamp and hand wheel, and are shipped pre-assembled. Angular drives with keyed/grooved shafts are available for motor interfaces with increased torque transfers.- For rotary transmissions of 90°
- Flexible adjusting to the installation position with continuous angular adjustment
- Clamping using set screw
- Max. drive torque 3Nm
Angular drives for XY-tables
Configure custom lead screw linear system online
- Customise your XY lead screw linear system in just a few steps
- Optional configuration of an individual drive pin
- Automatic generation of a 3D model of the linear system
- Export of the linear system in many different 2D and 3D formats
- 2D dimensional drawing of the module as a PDF
- Download parts list as PDF file
- Add to shopping cart and submit order or request a quotation online
Configure your drive system


